
Table of Contents
Owning a home or running a workplace in Fresno can give you a sense of security. But did you know that there are common electrical hazards that can put this safety at risk? It’s not just electricians who need to understand electrical safety – it’s important for everyone. By knowing how to stay safe around electricity, we can prevent accidents, fires, and even deaths caused by electrical problems.
Electrical dangers can be found in every part of our homes and workplaces, from the living room to the office space. These hazards can be as simple as having too many things plugged into one outlet or as complicated as having old wiring that’s no longer safe. Knowing about these risks and taking steps to fix them can make your Fresno homes and workplaces much safer places to be.
At Electriciansfresno.com, we’ve been serving the Fresno community for over 15 years. We understand how crucial it is to protect against these potential dangers. That’s why we’re here – to help you learn about common electrical hazards and find practical ways to make them less risky. Together, we can all work towards creating safer living and working environments for everyone in Fresno.
1. Electrical Hazards in Homes
Electrical hazards at home are often hidden, waiting silently until they cause residential fires. One important thing to think about is how to keep your home safe from electrical fires, which can cause significant damage and injuries.
Regular Wiring Inspections
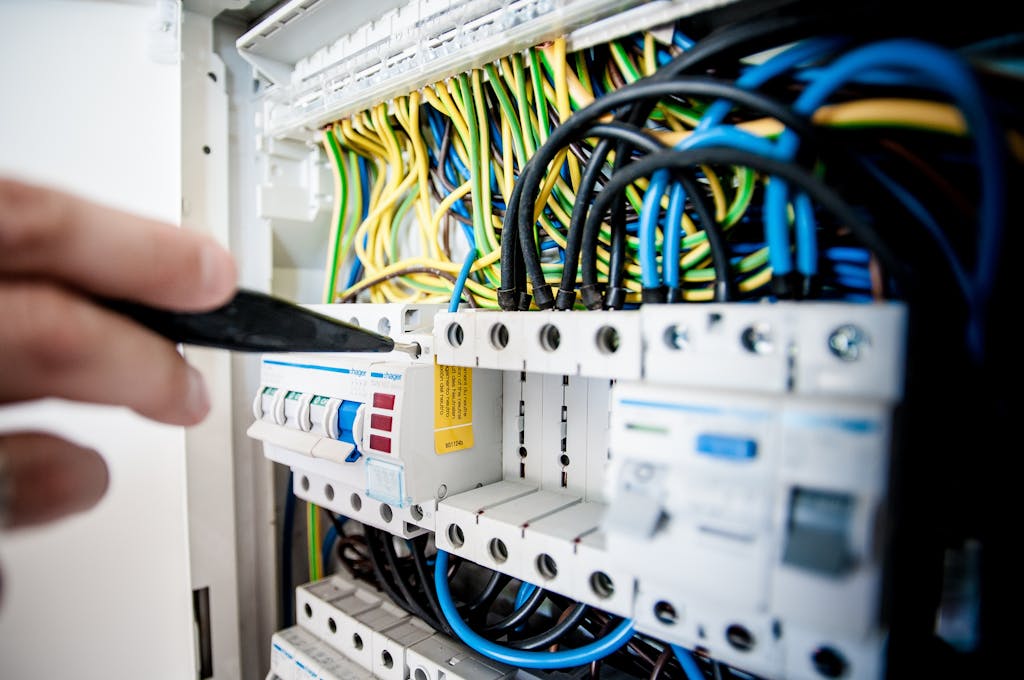

It’s crucial to have a professional electrician inspect your home wiring on a regular basis. Over time, wiring can wear out or become outdated, creating dangerous situations if not addressed. Regular inspections help identify potential problems early on and prevent major issues in the future.
Safe Use of GFCI Outlets and Surge Protectors
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) outlets and surge protectors are essential for electrical safety at home. Here’s how they work:
- GFCI outlets: These outlets automatically shut off power when they detect electricity flowing through unintended paths, such as water or a person. They provide extra protection against electric shocks.
- Surge protectors: These devices safeguard your electronic devices from sudden voltage spikes that could harm them. They divert excess electricity away from your devices, keeping them safe.
Power Strip and Extension Cord Safety Guidelines
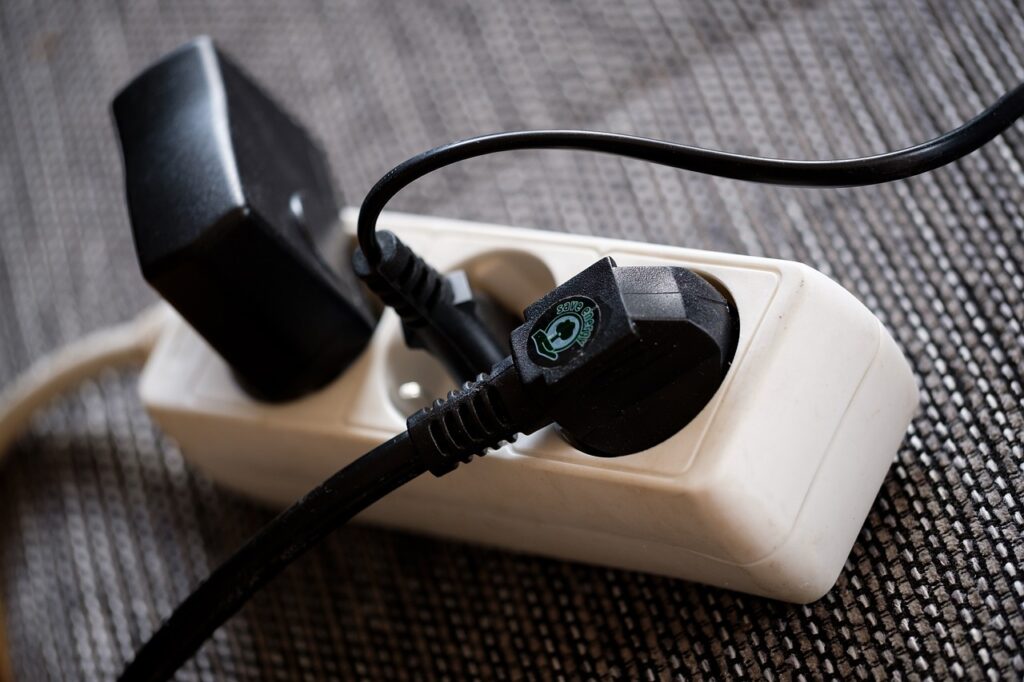

Power strips and extension cords are commonly used in households, but they can be dangerous if not used correctly. Follow these guidelines to ensure their safe use:
- Avoid overloading power strips and extension cords with too many devices plugged in.
- Don’t connect multiple extension cords or power strips together in a series (also known as “daisy-chaining”).
- Make sure cords are not placed under rugs or heavy furniture where they can get damaged or overheated.
Identifying and Fixing Malfunctioning Appliances
Malfunctioning appliances can pose a serious electrical hazard. Pay attention to warning signs such as:
- Circuit breakers frequently tripping
- Lights flickering
- Unusual noises coming from appliances
If you notice any of these signs, it’s important to have the appliance checked and repaired by a professional as soon as possible.
Remember, being proactive about these potential hazards is the first step in creating a safer home environment.
2. Electrical Hazards in Workplaces
It’s crucial to prioritize electrical safety while working. This goes beyond just protecting property; it’s about saving lives. One small mistake can lead to serious injuries or even death from electric shocks.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established guidelines to promote electrical safety in the workplace. Following these standards is key to reducing the chances of accidents and creating a safer environment.
Electrical Dangers in Construction Jobs
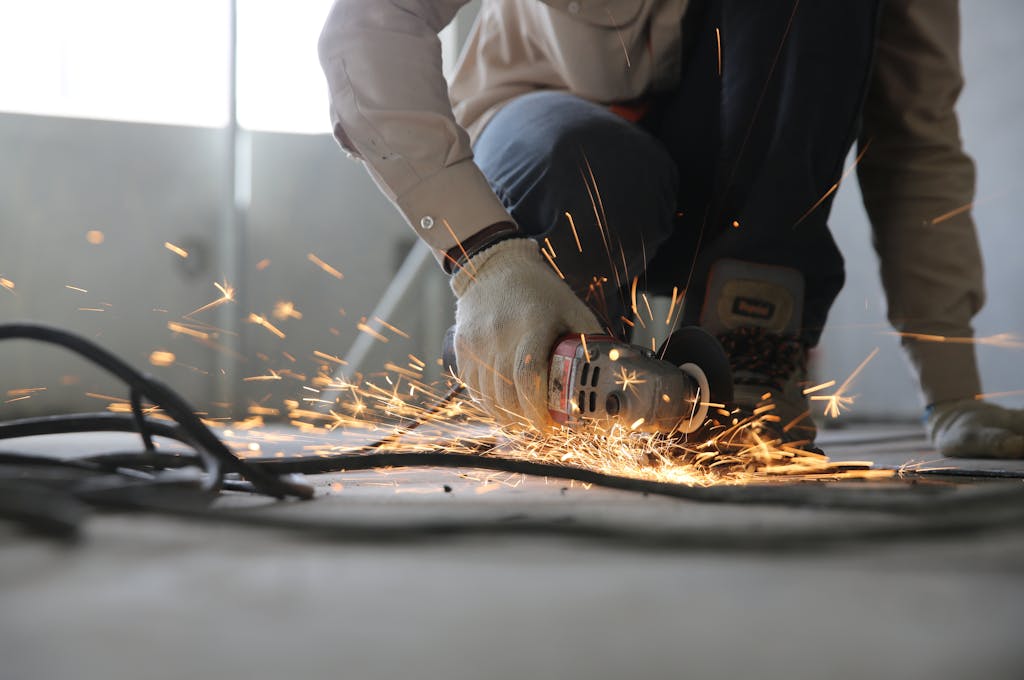

Construction sites are known for their high-risk nature, especially when it comes to working with electricity. Here are some potential hazards to watch out for:
- Exposed wiring: Loose or damaged wires can increase the risk of electrocution.
- Unsafe equipment: Faulty or outdated tools can be dangerous when used near power sources.
- Power supply issues: Overloaded circuits or faulty connections may lead to electrical fires or shocks.
To mitigate these risks, construction workers should:
- Conduct regular inspections of the site to identify and address any electrical hazards.
- Provide comprehensive training on proper handling and use of tools.
- Strictly follow safety protocols, such as wearing personal protective equipment (PPE) and using lockout/tagout procedures when working on electrical systems.
Precautions When Working Near Overhead Power Lines
Working in proximity to overhead power lines requires extra caution due to the high voltage involved. Here’s what workers should keep in mind:
- Maintain a safe distance: Always stay at least 10 feet away from power lines, both horizontally and vertically.
- Use non-conductive tools: When necessary, opt for insulated or fiberglass-reinforced tools that reduce the risk of electric shock.
- Be mindful of height restrictions: Ensure that ladders, cranes, or other tall equipment never come too close to overhead lines.
Safe Handling of Electrical Tools and Equipment

Various industries heavily rely on electrical tools and equipment for their operations. While these devices are essential, they can also be hazardous if not used correctly. Here are some safety practices to follow:
- Regular inspections: Check tools for any signs of damage or wear, such as frayed cords or broken switches. Replace or repair them immediately.
- Proper maintenance: Clean and lubricate equipment as recommended by the manufacturer to prevent malfunctions.
- Responsible usage:
- Avoid overloading power outlets or extension cords, as this can lead to overheating and electrical fires.
- Never operate tools with wet hands or in wet/damp conditions, as water increases the risk of electric shock.
By focusing on these areas – understanding OSHA standards, addressing construction site hazards, adopting safety measures around power lines, and managing tools effectively – workplaces can be made significantly safer from common electrical hazards.
3. Common Types of Electrical Hazards
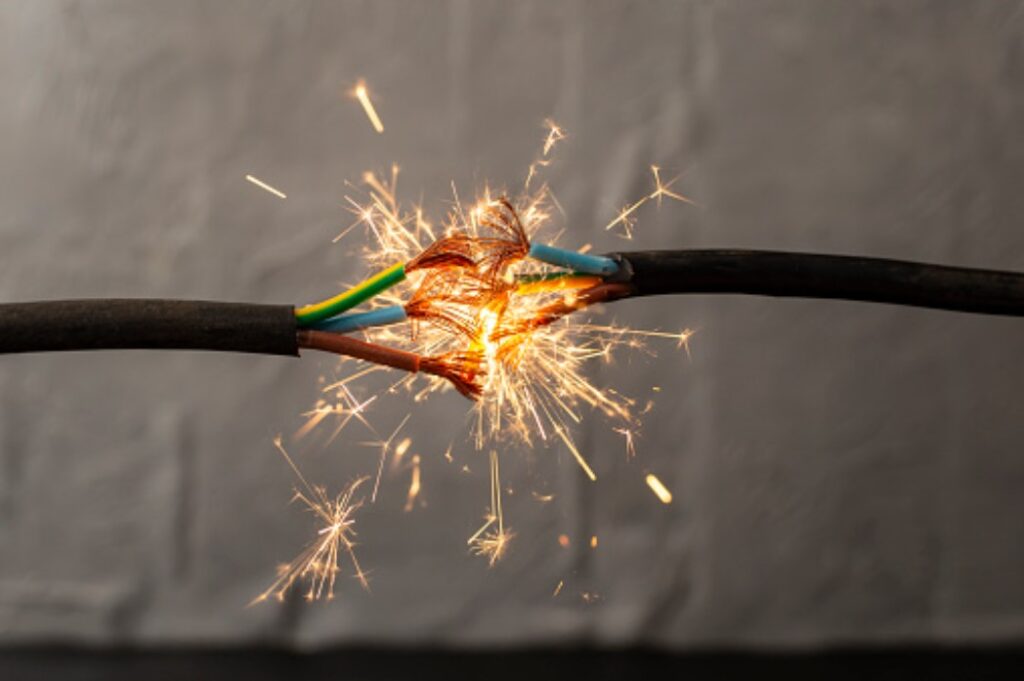
Recognizing and mitigating potential electrical hazards is essential for safety at home and in the workplace. Various risks lurk around, and being aware of them can prevent accidents and ensure a safe environment for everyone.
Damaged Electrical Tools and Equipment
One of the main sources of electrical hazards is damaged tools and equipment. Here are some common examples:
- Damaged Cords: Frayed wires or damaged power cords can result from overuse or mishandling. Such damage can expose live wires, leading to shocks, short circuits, or even fires.
- Inadequate Wiring: An often-overlooked hazard is inadequate wiring. Older homes may have wiring that cannot handle modern electrical demands, posing a significant risk of overheating and fire.
- Overloaded Circuits: Too many appliances plugged into a single outlet can overload circuits. Overloading not only damages the electrical system but also poses a fire hazard.
- Exposed Electrical Parts: Exposed wires or electrical components are dangerous because they could lead to electric shock upon contact.
Examples of Common Home Electrical Hazards to Watch Out For:
Here are some specific examples of electrical hazards that commonly occur in homes:
- Damaged Cords : Regularly check cords for signs of wear. Replace or repair damaged cords immediately. Do not run cords under carpets where damage can go unnoticed.
- Outdated Wiring : Have an electrician inspect your wiring, especially if you live in an older home. Update wiring to meet current codes and accommodate modern appliances safely.
- Overloaded Outlets : Use only one high-wattage appliance per outlet. Consider having additional outlets installed by a professional if necessary.
- Water Exposure : Keep electronics and appliances away from water sources. Immediately shut off power at the circuit breaker if water contacts electrical systems or appliances.
By staying vigilant about these hazards—damaged electrical tools and equipment, inadequate wiring, overloaded circuits, exposed electrical parts—you can create a safer living and working environment. Regular inspections by qualified professionals are vital in identifying and correcting these issues before they lead to more serious consequences.
Educating family members and employees about these risks will empower them to recognize danger signs early on. Shared knowledge is a powerful defense against electrical hazards that threaten our homes and workplaces every day.
4. Ensuring Electrical Safety in the Workplace

Creating a safe workplace goes beyond wearing safety gear and following general rules. To promote electrical safety at work, it’s important to:
Lockout/Tagout Procedures
During maintenance work, it is crucial to follow lockout/tagout procedures. These steps involve:
- Turning off and disconnecting electrical equipment.
- Securing it with a lock or tag to prevent accidental startup.
- Verifying that the equipment is de-energized before starting any work.
This process helps prevent unexpected energization of equipment, which can lead to serious injuries or even fatal accidents.
Extension Cord Safety
While extension cords can be useful, they should be used properly to avoid hazards. Here are some guidelines for extension cord safety:
- Choose heavy-duty extension cords that are suitable for the specific appliance or tool.
- Avoid placing extension cords across walkways or hiding them under carpets where they can be tripped over or damaged.
- Refrain from connecting multiple extension cords together (known as “daisy-chaining”) as it can overload the cords and increase the risk of fire.
Grounding of Equipment
Proper grounding of electrical equipment is essential for safety. This means connecting the equipment to a grounding conductor, such as a ground wire or metal conduit, which provides a path for electrical faults to safely flow into the ground. Grounding helps prevent electric shock in case of equipment malfunction or insulation failure.
Insulation
Insulation acts as a protective barrier between electricity and its surroundings. It prevents electrical energy from escaping into areas where it could cause harm. To maintain effective insulation:
- Ensure all wires, cables, and cords have intact insulation.
- Check equipment and tools for any signs of damaged insulation, such as frayed wires or cracked casings.
- Promptly repair or replace any faulty insulation to prevent electrical accidents.
By implementing these measures, workplaces can significantly reduce the risk of electrical hazards and create a safer environment for everyone involved.
Conclusion
Electricity powers our lives in Fresno, both at home and at work. It’s important to understand how to manage electrical risks in these environments to ensure safety. The information provided here is meant to be a helpful resource for Fresno residents, highlighting potential hazards and offering proactive solutions.
The Importance of Electrical Safety
Being aware of electrical safety is crucial because:
- Electricity is Invisible: Unlike other hazards, such as fire or sharp objects, electricity cannot be seen. This makes it even more important to understand its potential dangers and take preventive measures.
- Electrical Incidents Can Cause Serious Harm: Electrical accidents can result in severe injuries or even fatalities. By prioritizing safety, we can reduce the risk of such incidents occurring.
- Prevention is Key: Many electrical accidents can be prevented with proper knowledge and precautions. By being proactive, we can create safer environments for ourselves and others.
Tips for Electrical Safety
Here are some practical tips that everyone can follow to enhance electrical safety:
- Stay Informed: Keep yourself updated with the latest safety guidelines and technologies related to electricity.
- Schedule Regular Inspections: Arrange for professional inspections of electrical systems in your home or workplace on a regular basis. This helps identify any potential issues early on.
- Handle Tools and Equipment Properly: Follow recommended practices when using power strips, extension cords, and other electrical tools. Avoid overloading circuits or using damaged equipment.
- Install Safety Devices: Consider installing Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) in areas where water is present, such as kitchens and bathrooms. These devices quickly shut off power in case of a ground fault.
- Protect Against Surges: Use surge protectors for sensitive electronic devices to prevent damage from power surges.
- Ensure Proper Grounding: Verify that electrical outlets are properly grounded to reduce the risk of electrical shocks.
- Teach Children about Electrical Safety: Educate children about the potential dangers of electricity and teach them how to use it safely.
The Role of Individuals in Electrical Safety
It’s important for each individual to take responsibility for their own safety and contribute to a culture of electrical safety in Fresno:
- Homeowners: Regularly check electrical systems, address any issues promptly, and create a safe environment for your family.
- Employers: Provide proper training to employees regarding electrical hazards and ensure compliance with safety regulations in the workplace.
- Employees: Follow safe work practices when dealing with electricity, report any faulty equipment or potential hazards to supervisors, and actively participate in safety programs.
Together, We Can Prevent Electrical Accidents
By implementing these measures and promoting awareness about electrical safety, we can make a significant impact in reducing electrical risks:
- Protecting lives: Ensuring the well-being of ourselves, our loved ones, and fellow community members.
- Safeguarding property: Preventing damage or loss due to electrical fires or accidents.
- Supporting productivity: Creating a safe working environment where employees can perform their tasks without fear of electrical hazards.
Let’s work together towards a safer Fresno, where everyone can enjoy the benefits of electricity without compromising on safety.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What are some common electrical hazards in homes?
Common electrical hazards in homes include residential fires, issues with wiring that require regular inspection, the safe use of GFCI outlets and surge protectors, guidelines for power strip and extension cord safety, and identifying and fixing malfunctioning appliances.
How can homeowners protect their homes from electrical fires?
Homeowners can protect their homes from electrical fires by ensuring regular wiring inspections, using GFCI outlets and surge protectors, following guidelines for power strip and extension cord safety, and promptly identifying and fixing malfunctioning appliances.
What are some electrical hazards in workplaces?
Electrical hazards in workplaces include the risk of electrocution, especially in construction jobs and near overhead power lines, as well as dangers associated with electrical tools and equipment. It is important to understand OSHA’s standards for workplace electrical safety.
What are some common types of electrical hazards to watch out for?
Common types of electrical hazards include damaged electrical tools and equipment, inadequate wiring, overloaded circuits, and exposed electrical parts. It is important to recognize potential electrical hazards anywhere, including in home settings.
What are some comprehensive approaches to workplace electrical safety?
Comprehensive approaches to workplace electrical safety include implementing lockout/tagout procedures during maintenance work, using extension cords safely in a commercial setting, ensuring proper grounding of equipment, and understanding the role of insulation in preventing electrical accidents.
How can Fresno residents stay safe from electrical hazards?
Fresno residents can stay safe from electrical hazards by empowering themselves with knowledge about common electrical risks in homes and workplaces. This includes understanding the importance of regular inspections, safe usage of electrical devices, and recognizing potential hazards.